Indirect Thermal Desorption Systems
THERMA-FLITE SCREW PROCESSORS: HIGH-EFFICIENCY, LOW PROFILE.
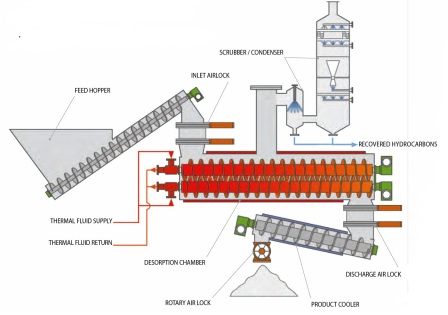
Therma-Flite thermal desorption systems are turn-key, and include all necessary components to:
- Hold and meter feed stock into the desorption chamber;
- Provide an airlock to the inlet and discharge of the unit;
- Cool the material exiting the desorption chamber;
- Condense volatiles for collection.
Tank Bottom Sludge and Soil Remediation
CONDENSE AND RECOVER HYDROCARBONS IN ONE EASY STEP.
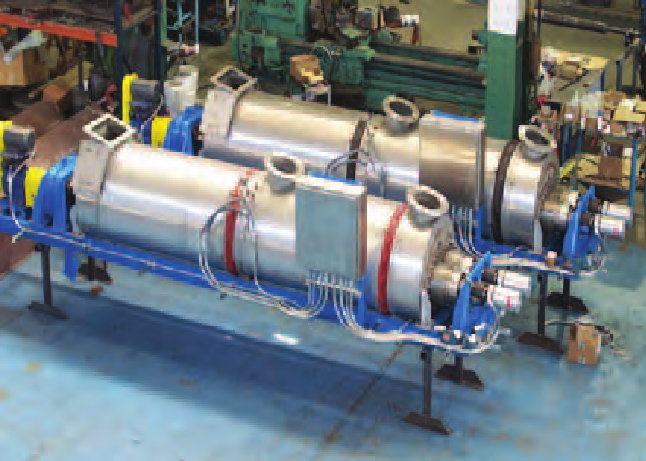

Therma-Flite Holo-Scru® desorption units heat residual material to 1,000-plus-degrees Fahrenheit, so that hydrocarbons and water vapor are condensed and recovered.
These tank bottoms may also be discarded after they have been thermally treated to recover hydrocarbons. Multi-stage systems make the process even simpler by removing water in one unit, while removing hydrocarbons in a second.
There are Therma-Flite Holo-Scru® installations that have been in operation for more than 20
years processing tank bottom sludges and other feed stocks such as soil and catalyst fines.
Drill Cuttings Dryers
PROCESS 1.5 TO 500 TONS PER DAY WITH 99.5% HYDROCARBON RECOVERY.
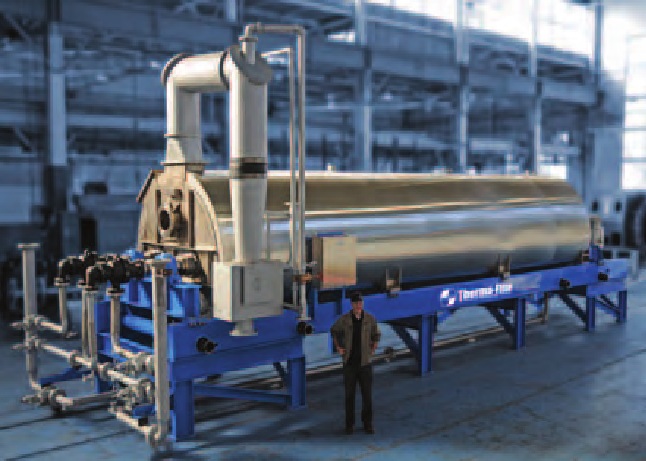

Therma-Flite Holo-Scru® thermal desorption systems volatilize and recover 99.5% of hydrocarbons from drilling mud. Oil, diesel and other synthetics are often used as lubricants in drilling for natural gas. After this mud is recovered and centrifuged, the slurry typically contains high levels of water, diesel, even crude oil.
Holo-Scru® processes can accept feed stock with hydrocarbon percentages greater than 70%,
effectively collecting and condensing water, diesel and other hydrocarbon vapors. In applications
such as natural gas drilling where diesel and water constitute the liquid phase, diesel is typically filtered, then resold or reused as a lubricant for future drilling.
Therma-Flite units in operation in the U.S. process drill cuttings from shale drilling; This feed stock is generally 10% to 30% diesel, and 20% water. Recovery rates for diesel typically range from 97% to 99.5%.
Hazardous Waste Processing
DELISTING RESOURCE CONSERVATION AND RECOVERY ACT (“RCRA”) WASTE.
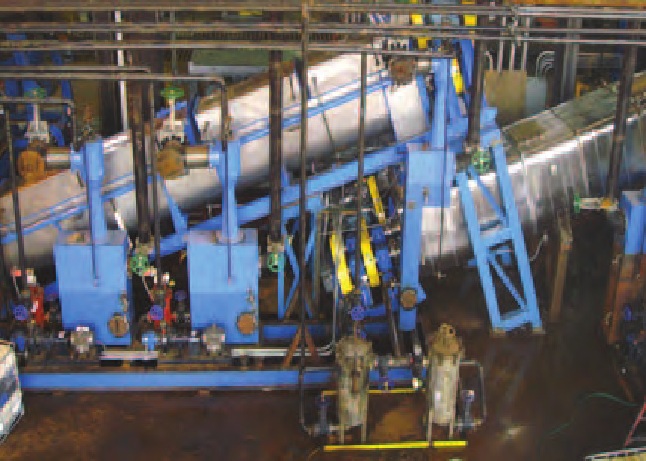

Therma-Flite Holo-Scru® desorption units are excellent for delisting RCRA waste. Drums, cans, glass and plastic containers are just some of the items that carry hydrocarbon-laden materials such as paint, perfume, degreaser, oil, resins, and hair spray.
Such feed stock is typically shredded to 2-inch minus in order to add easily to the desorption unit. Holo-Scru handles the shredded metal and glass quickly and efficiently. Sticky materials are also handily-processed by virtue of the system’s self-cleaning, rotor design. Process temperatures between 850 and 1,200-degrees Fahrenheit (depending on feed stock requirements) volatilize all hydrocarbons.
The heart of the systems, the desorption unit, includes intermeshed Holo-Scru® rotors. In this chamber, feed stock is heated under a slight negative pressure in a sealed, anaerobic environment; heating is indirect. Thermal fluid is circulated throughout the Holo-Scru® rotors and outer jacket of the desorption chamber. The proprietary Holo-Scru® dual rotor design is self-clearing and feed stock which might otherwise bake on to the rotors, is easily removed. Different mixing programs may be set in the Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) which will increase the heat transfer into the feed stock.
A variety of heat transfer fluids may be used to heat product up to 850-degrees Fahrenheit. A second stage system can be incorporate to heat the product to above 1200-degrees Fahrenheit. Most feed stocks may be de-volatilized to less than .05% remaining hydrocarbons. As the heated solids exit the desorption chamber, they pass through a second airlock and into a cooling screw conveyor. In the cooling screw, solids are indirectly cooled by circulating water through the jacketed wall of the screw. The temperature is further reduced by direct-contact quench cooling via atomizing sprays along the top of the cooling screw housing. The vapors exit the unit into a Venturi-effect, multi-stage condenser. Cooled and filtered condensate is used as the condensing fluid. The Venturi-effect condenser is highly-efficient with less than .01% hydrocarbons remaining in the non-condensable stream. The non-condensable stream is released through a duct to the air intake on the diesel generator providing the unit’s electrical power.
- Maximum product temperature: 900-degrees Fahrenheit;
- Maximum operating pressure: 350 psi;
- Maximum operating vacuum: 50 millitorr.
Single-stage desorption unit